-
- Oct 20
-
melbourneconcretepumping

- 0
The Best Practices for How to Organise a Concrete Pump
Looking to organize a concrete pump? This guide will show you how to organise a concrete pump, select the right pump, prepare your site, and manage the entire pumping process. From setup to post-pumping procedures, find the steps to ensure an efficient and successful concrete pour.
Key Takeaways
- Concrete pumps streamline concrete delivery, enhancing efficiency and precision in construction projects, with ground pumps suitable for smaller tasks and boom pumps for larger-scale jobs.
- Proper preparation and management of the site, including ensuring clear access for equipment and assessing ground conditions, are essential for successful concrete pumping operations.
- Effective coordination among personnel is crucial for the organization of concrete pumping operations, ensuring smooth communication and preventing delays during the concrete pour.
Understanding Concrete Pumps

Concrete pumps have revolutionized the construction industry by making concrete delivery and pouring more efficient and precise. Construction utilizes two primary types of concrete pumps: ground pumps and boom pumps. Ground pumps are ideal for smaller projects like sidewalk paving, while boom pumps are designed for larger projects such as highways and high-rise buildings. Concrete pumping aims to streamline the delivery and pouring process, eliminating the need for manual transport methods like wheelbarrows.
The versatility of concrete pumps cannot be overstated. They can be used in a wide range of applications, from creating uniform slab foundations to enhancing access to difficult areas on a construction site. Whether you’re working on parking structures, in-ground pools, or any other project, concrete pumps can ensure that you place concrete precisely where it’s needed.
By enabling quick and accurate concrete delivery, concrete pumps have significantly enhanced construction efficiency. This speeds up the process while maintaining structural integrity. Understanding the different types of pumps and their applications helps in choosing the right equipment for specific needs, ensuring a successful good pump mix concrete pour.
Preparing Your Site for a Concrete Pump

A smooth and efficient concrete pumping operation starts with thorough preparation. Begin by ensuring that your site is clear and accessible. This means assessing any narrow driveways, parked cars, or overhead obstructions that could impede the movement of the concrete pump and mixer trucks. Both the pump and the concrete mixer trucks need clear access to reach the setup area without any issues.
Choose a flat, secure surface for the concrete line pump, ensuring easy access for the mixer truck to reach the hopper. Ensure clear pathways and ample room for mixer trucks to maneuver, making the concrete delivery process seamless. Safe access for the concrete pump and mixer trucks must be arranged to facilitate an efficient pouring process.
Thorough preparation and planning are essential. Check for potential hazards and ensure the site can accommodate the equipment’s size and height. Taking these steps ensures a successful concrete pump pour, avoiding unnecessary delays or complications.
Ground Line Pump Setup
Setting up a ground line pump involves several steps to prepare the equipment for operation. Ground pumps are particularly useful for difficult locations, such as backyards with limited access. Start by checking the engine and oil levels, inspecting the ‘S’ tube for blockages, and ensuring all hoses are properly stretched and connected.
Ensure timbers and pads are adequately sized to support the concrete pump and prevent subsidence during operation. Attach the suction hose to the pump and connect the chute to the hose, using lubricant to ease the connection. Fill a container and check for leaks to conduct a water test, ensuring the assembly is secure before use.
Prime the concrete pump by using slurry or oil and stroking the pump several times to coat the hoses and prevent clogs. Properly packing away ancillary equipment before the pump leaves the site is crucial for efficiency. Following these steps ensures that your ground line pump is set up correctly and ready for a successful concrete pump pour.
Boom Pump Setup
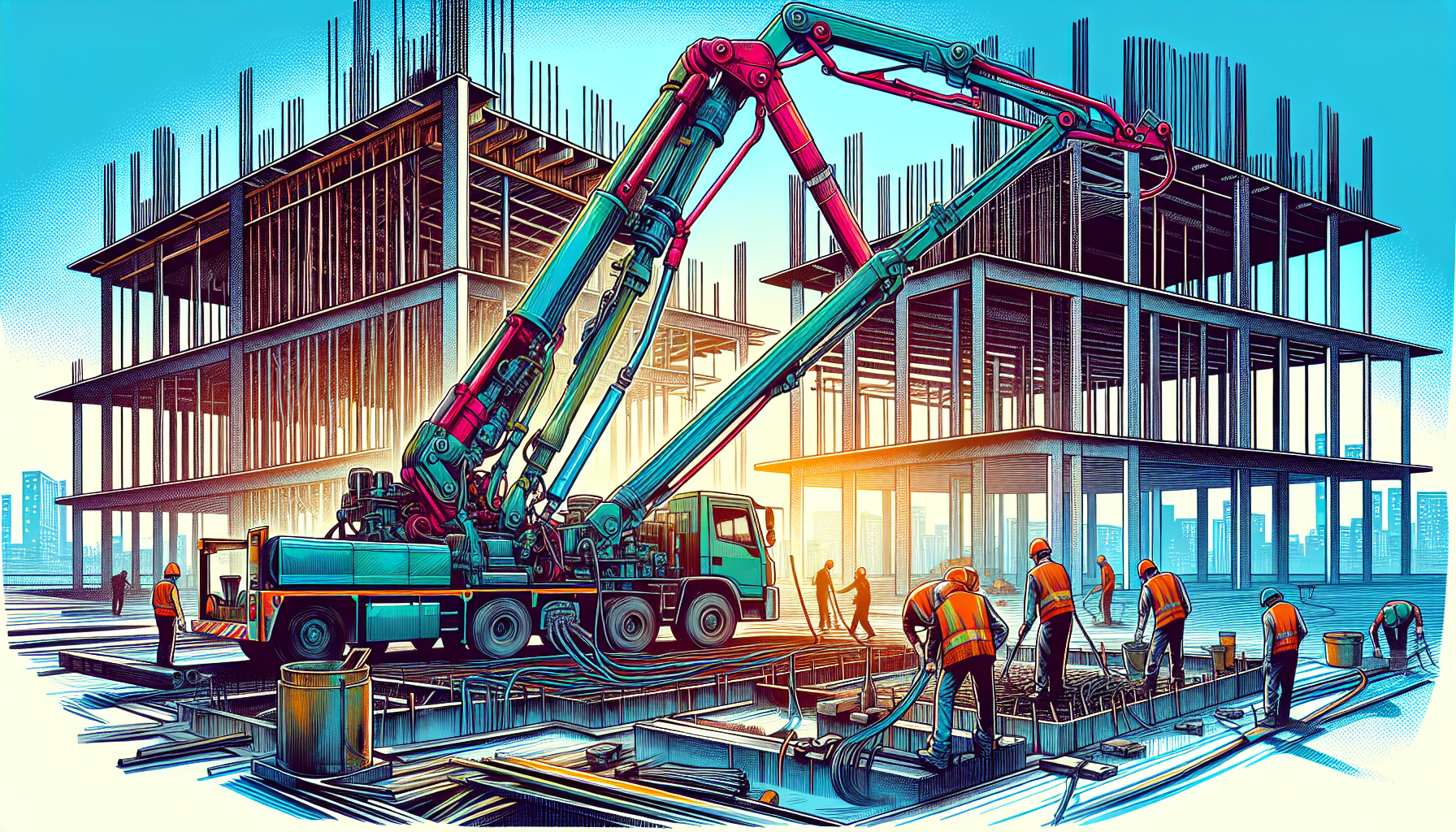
Boom pumps are ideal for high-rise projects and other large-scale construction tasks. Setting up a boom pump requires careful planning and consideration of ground conditions. The setup area must be level and capable of supporting the highest outrigger loadings for safety. Assess the ground’s bearing capacity to support the maximum pressure exerted by the pump’s outriggers.
Ensure the pump set up area is free of obstructions and level to mitigate high-pressure risks. Boom pumps allow concrete placement at elevated locations, making them essential for projects like bridge deck etc and high-rise buildings. Proper setup ensures both safety and efficiency in the pumping operation.
Following these guidelines ensures your boom pump is set up correctly and the operation proceeds smoothly. Attention to detail is crucial for a successful pour, especially in complex projects requiring precise concrete placement.
Ensuring a Good Supply of Concrete

A continuous supply of concrete prevents delays during construction projects. Concrete pumps perform consistently even in adverse weather, ensuring project timelines are met. Efficient concrete pump pours require careful management of supply logistics.
Mixer chutes typically extend about 2.4 meters from the back of the truck, influencing how concrete is directed to the intended pour site. Clear and safe access for mixer trucks is crucial to maintain a steady flow of concrete. Proper coordination and planning help avoid supply interruptions, ensuring a smooth operation.
Consulting the CPA good practice guide provides valuable insights into maintaining a good concrete supply and managing logistics effectively. Following these best practices ensures your concrete pumping operation runs smoothly and efficiently.
Organizing the Pumping Operation

Organizing a concrete pumping operation requires careful planning and coordination. Place the concrete pump properly to minimize the distance between the source and the pour site, ensuring efficient delivery. Effective communication between the pump operator and the contractor is crucial before setup to align details and expectations.
Managing excess grout is an important aspect of the operation. Direct it back into the hopper or use a cleanout method to prevent waste. Deposit excess grout properly instead of mixing it into the pour. Personnel should be aware of the risks associated with high-pressure pumping and pump excess grout to ensure efficiency.
Automation of concrete pumps reduces the required workforce, making operations more efficient. Effective organization of the pumping operation ensures a successful pour and avoids unnecessary complications.
Managing the Concrete Mixer Truck
Managing the concrete mixer truck is crucial for an efficient concrete pump pour. Plan for potential excess concrete in advance to avoid complications with returns or disposal fees. Clean the mixer chutes after discharging concrete to prevent blockages in the pump.
A competent team is necessary to lay the concrete effectively throughout the operation. The team should be well-coordinated and skilled in handling the concrete to ensure that the project proceeds smoothly. Effective management of the concrete mixer truck ensures a successful pour and avoids delays or complications.
Ensure the mixer leaves the site clean and ready for the next job as part of proper management. Following these best practices ensures your concrete pumping operation runs smoothly and efficiently.
Coordinating with the Concreting Gang
Effective coordination with the concreting gang is essential for a successful operation. A competent team is crucial for managing the concrete placement during pumping operations. Proper communication and coordination with the gang ensure everyone is aligned on work requirements and expectations.
Early planning is crucial for safe operations and should involve all stakeholders. Consulting the Concrete Pumping Code of Practice 2019 provides valuable insights into team roles and responsibilities. Effective coordination with the gang ensures a successful pour and avoids unnecessary complications.
Properly briefing the gang on the job sheet ensures alignment on tasks and expectations. This alignment is crucial for the operation’s success and ensures the project proceeds smoothly.
Dealing with Ground Conditions
Managing ground conditions is essential to ensure the stability and safety of the setup. Ground conditions can change over time due to factors like saturation, soil type, and slope. Improper ground conditions can cause mobile concrete pumps to tip over, resulting in injuries or damage.
Avoid setting up pumps on previously disturbed or back-filled ground to maintain stability. Regular checks of outrigger stability are essential for safe operation and accident prevention. Effective assessment and management of ground conditions ensure a safe and stable setup for your pump.
Suitable ground conditions are crucial for the success of the pumping operation. Following these best practices helps avoid potential hazards and ensures a smooth and efficient pour.
Post-Pumping Procedures
Post-pumping procedures are crucial for maintaining equipment and site cleanliness. Cleaning the pump and its pipeline typically takes about an hour after the operation. This involves pouring water into the hopper and running it to clear out any remaining concrete from the hoses.
Proper disposal of excess grout maintains site cleanliness and adherence to regulations. After unloading, clean the mixer truck chutes to prevent blockages that could affect concrete quality. Following these post-pumping procedures ensures your equipment is well-maintained and ready for the next job.
Proper cleaning and maintenance of the pump and all the ancillary equipment are crucial for longevity and success in future projects. Following these best practices ensures your concrete pumping operation runs smoothly and efficiently.
Summary
In summary, organizing a concrete pump involves several crucial steps, from understanding the different types of pumps to preparing the site, setting up the pump, and managing the concrete supply. Proper coordination with the concreting gang and careful management of ground conditions are essential for ensuring a successful concrete pump pour.
By following the best practices outlined in this guide, you can ensure that your concrete pumping operation runs smoothly and efficiently. From the initial setup to post-pumping procedures, each step is important for the success of the project.
With careful planning and attention to detail, you can master the art of concrete pumping and ensure the success of your construction projects. Remember, the key to a successful concrete pump pour lies in preparation, coordination, and proper management.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main types of concrete pumps used in construction?
The main types of concrete pumps used in construction are ground pumps, suitable for smaller projects like sidewalks, and boom pumps, which are designed for larger projects such as highways and high-rise buildings. Thus, selecting the appropriate pump type is crucial based on the project scale.
How do I prepare my site for a concrete pump?
To effectively prepare your site for a concrete pump, ensure the area is clear, accessible, and features a flat surface for setup. Additionally, coordinate with mixer trucks to maintain clear pathways and adequate maneuvering space.
What steps are involved in setting up a ground line pump?
Setting up a ground line pump requires checking the engine and oil levels, inspecting the ‘S’ tube for blockages, attaching the suction hose, conducting water tests, and priming the pump with slurry or oil. It is crucial to follow these steps to ensure proper functioning and efficiency.
How do I manage the concrete mixer truck during a pumping operation?
To effectively manage the concrete mixer truck during a pumping operation, ensure you have a plan for excess concrete, clean the mixer chutes after discharging, and maintain a skilled team to properly lay the concrete. This approach will enhance operational efficiency and maintain project quality.
What are the post-pumping procedures?
Post-pumping procedures are crucial for site cleanliness and equipment longevity and include cleaning the pump and pipeline, properly disposing of excess grout, and cleaning the concrete mixer truck’s chutes to prevent blockages.
e area is level and free of obstructions to mitigate risks associated with high pressure.
Ensuring a Good Supply of Concrete
- Maintaining a continuous concrete supply is crucial for preventing delays during construction projects.
- Mixer chutes typically extend about 2.4 meters from the back of the truck, influencing how concrete is directed to the intended pour site.
- Concrete pumps can perform consistently in adverse weather, maintaining project timelines.
Organizing the Pumping Operation
- Proper placement of concrete involves ensuring the pump is positioned to minimize the distance between the source and the pour site.
- Using the end hose effectively requires maintaining a steady flow and being aware of the hose’s placement to avoid obstruction.
- Excess grout should be managed by directing it back into the hopper or using a cleanout method to prevent waste.
- Excess grout should ideally be disposed of properly rather than pumped into the concrete pour.
- Excess grout should be pumped to waste instead of being mixed into the concrete pour.
- Personnel should be aware of the risks associated with high-pressure pumping and end hose usage.
- Automation of concrete pumps reduces the required workforce, making operations more efficient.
- Effective communication between the pump operator and the contractor is crucial before the pump setup.
Managing the Concrete Mixer Truck
- Managing the concrete mixer truck is crucial for ensuring an efficient concrete pump pour.
- Planning for potential excess concrete should be done in advance to avoid complications with unwanted returns or disposal fees.
- Cleaning the mixer chutes after they discharge is important to prevent blockages in the pump.
- A competent team is necessary to effectively lay the concrete throughout the pumping operation.
Coordinating with the Concreting Gang
- A competent team is essential for managing the concrete placement during pumping operations.
- Having a skilled concreting crew is essential for effectively laying concrete during a pumping operation.
- Having a skilled concreting team is crucial for the success of concrete pumping operations.
- It’s crucial to communicate the details outlined in the job sheet to the concreting gang to ensure everyone is aligned on the work requirements.
- Properly briefing the concreting gang on the job sheet ensures everyone is aligned on tasks and expectations for the project.
- Early planning is crucial for safe concrete pumping operations and should involve all stakeholders in the project.
- Consulting the Concrete Pumping Code of Practice 2019 is essential for understanding roles and responsibilities in concrete pumping operations.
Dealing with Ground Conditions
- Ground conditions can change over time and can be affected by factors like saturation, soil type, and ground slope.
- Improper ground conditions can lead to mobile concrete pumps tipping over, resulting in injuries or damage.
- Operators should avoid setting up concrete pumps on previously disturbed or back-filled ground to maintain stability.
- Regular checks of outrigger stability are essential to ensure safe operation and prevent accidents.
Post-Pumping Procedures
- After use, clean the pump by pouring water into the hopper and running it to clear out any remaining concrete from the hoses.
- After the pumping operation, it typically takes about an hour to clean the pump and its pipeline.
- At the end of the job, the pump operator needs to clean the pump and pipeline, which could take around an hour.
- After the pumping operation, it is essential to wash the pump at a designated spot to prevent concrete residue from hardening.
- Proper disposal of excess grout is necessary to maintain site cleanliness and adhere to regulations.
- After the concrete mixer truck unloads, the chutes must be cleaned to prevent blockages that could affect concrete quality.
melbourneconcretepumping